3xx redirect in sitemap are vital to SEO, yet can sometimes prove troublesome for both users and search engines alike. They may prevent users from reaching the URLs they require. To address these issues, check Ahrefs Sitemap Error Report and delete redirected pages from your sitemap.
Internal links
Internal links that redirect to incorrect permalinks can create various problems on a website, from poor user experience and high bounce rates to wasted crawl budget. Ahrefs’ Site Audit tool can identify these errors and assist you in correcting them by either removing broken links or setting up 3xx redirect in sitemap.
If your pages don’t exist within an XML sitemap and lack backlinks, Google may find them hard to discover – leading to an inevitable 404 error page and leading to user disappointment and leaving your site altogether. This situation can only harm user experience and SEO alike!
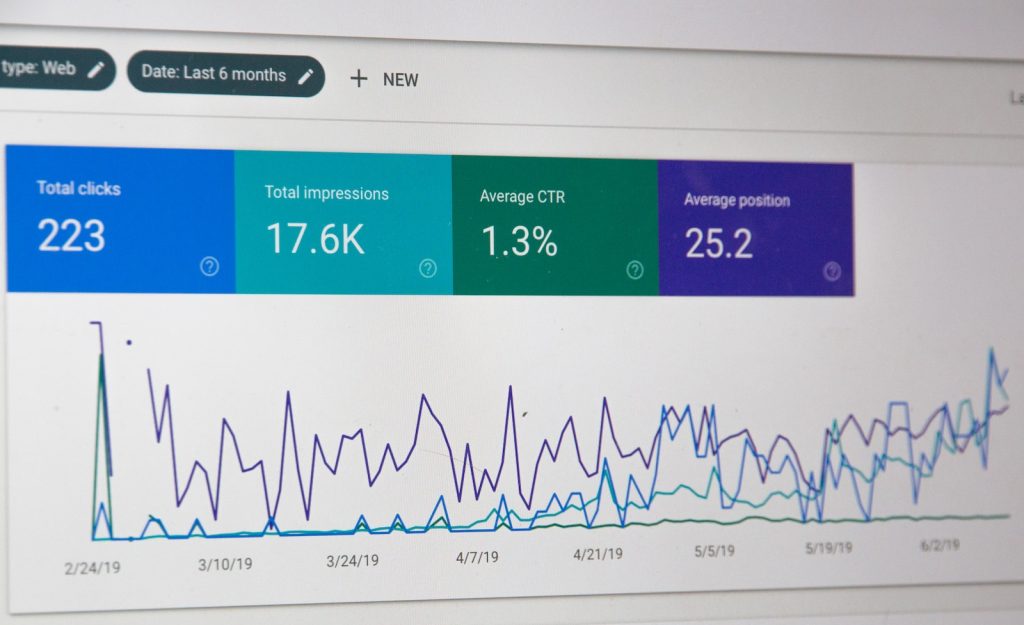
Doing a regular check of your XML Sitemap for any broken links and using Ahrefs’ XML Sitemap Tool can be very effective at this. Simply select your sitemap file from the list, click “Crawl & Analyze,” add “No. of dofollow backlinks” as a column in “Manage Columns,” sort your XML Sitemap using this column and identify any 404 pages!
One common issue occurs when a 3xx redirect in sitemap points to an incorrect page. This often happens when pages are moved or deleted from databases; either way, search engines send traffic directly to their original pages; however, since this traffic cannot be served due to being redirected away to an invalid URL, traffic from search engines will still reach them regardless. Using either 301 or JS redirection as solutions should solve the problem effectively.
Broken redirects
Broken redirects, pages that can no longer be reached by visitors or search engines, are one of the primary contributors to site speed issues and organic traffic loss, indexation issues. While avoiding redirects in general is the ideal solution, sometimes this isn’t possible so there are methods of fixing broken redirects and preventing their effects on SEO performance.
Ahrefs’ Site Audit provides an easy way of checking for 301 redirects on websites, scanning through them and listing every redirecting URL, making it simple to remove these from your sitemap and replace with permanent links. Google Analytics users can also filter organic sessions for 301s before reviewing the Overview report for results.
Screaming Frog or Lumar offers another effective method to identify broken redirects by scanning your site for links that redirect. This will enable you to detect and resolve any redirect chains; these occur when multiple redirections exist between initial and destination URLs resulting in poor user experiences and waste of crawl budget. To avoid this scenario, all links that redirect should be changed accordingly so they land at one final destination URL.
301 pages that receive organic traffic
Redirect chains can have serious repercussions for your website and speed, as they do nothing to spread value through linking equity. To eliminate redirect chains altogether, either use 301 redirects or replace internal links leading to redirect URLs with direct ones.
Redirecting with 301 redirects is the preferred solution as they’re permanent and pass PageRank. However, too many redirects could potentially slow down and negatively affect user experience; to prevent this problem from arising use a tool like Ahrefs Site Audit to quickly pinpoint problem pages.
Redirect loops are another common redirect issue. Redirect loops occur when one URL redirects back to itself or an earlier one in the chain, creating problems for both visitors and search engines alike, possibly blocking access to original pages or prompting too many redirect errors in browsers. To identify and address redirect loops on your site, check your Ahrefs Free Webmaster Tools account or Google Analytics’ Redirects report regularly for potential redirect loops.
Once again, your sitemaps should redirect organic visitors directly to their intended destinations or present a 404 error page, not redirect.
Redirect chains
Redirect chains and loops can be an immense SEO stumbling block, slowing page loads down significantly while harming search engine rankings and leading to lower site performance and an increased bounce rate. Search engines only have so much crawl budget to search, and if too many redirections occur they will stop looking altogether – something commonly caused during website migrations or relaunches; but they can also happen accidentally due to differences between HTTP vs. HTTPS URLs, www vs non-www URLs, trailing slash URLs etc.
As previously noted, you can fix redirect chains by running online tools such as Ahrefs’ Site Audit and Screaming Frog. These tools will identify all pages which form part of a redirect chain or loop; furthermore they list their final status: for example a page with 3xx status indicates how many redirections it had and its final destination.
If the final page cannot be reached, a 4xx or 5xx status code may be displayed. To resolve this, delete the redirect page and replace it with one that lives. Furthermore, make sure that internal links point towards its final destination URL, as well as eliminating external links that link back to it.