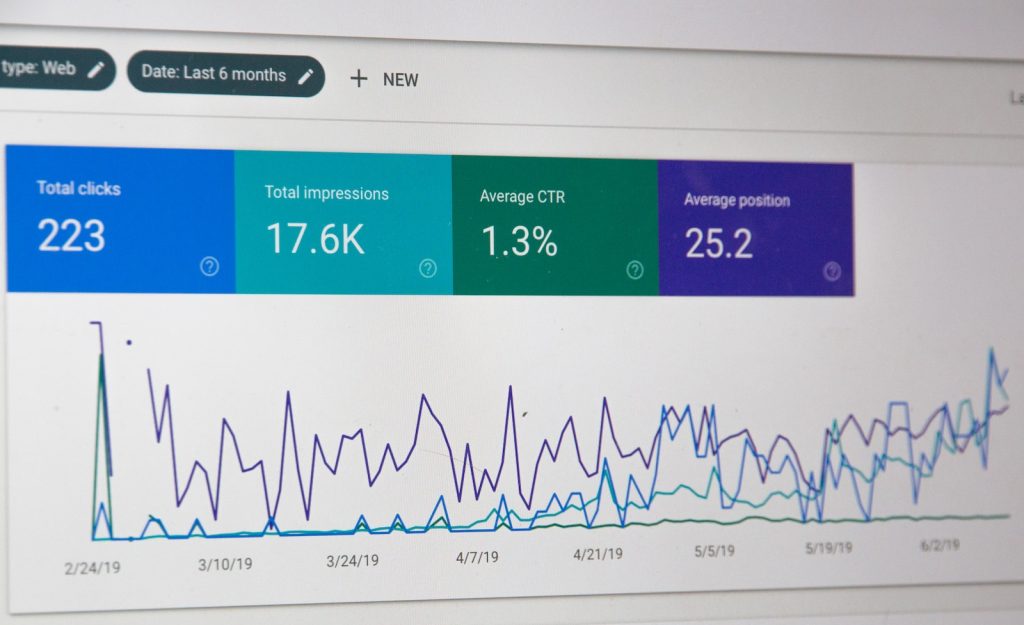
Did you know that over 90% of pages never get any traffic from Google? That’s often because they’re not indexed, making them invisible in search results. If your site’s pages are part of this ghost town, it’s time for a change. We’ll dive into the nitty-gritty of diagnosing and fixing the dreaded ‘pages not indexed‘ status in Google Search Console. From understanding the root causes to implementing effective solutions, we’ve got your back. Let’s turn those unseen pages into SEO goldmines.
Understanding Different Indexing Statuses
Crawled Statuses
Google Search Console shows various index statuses for your pages. “Crawled – currently not indexed” means Google has seen the page but hasn’t added it to its index. This could be due to quality issues or a temporary glitch.
“Crawled – currently not indexed” status can be confusing. It suggests that while Google’s bots have visited your site, they’ve chosen not to include those pages in search results yet.
Discovered Status
On the other hand, “Discovered – currently not indexed” indicates that Google knows about the URL but hasn’t crawled it yet. This might happen if your site has too many pages or if some are deemed less important.
Understanding this status helps prioritize which areas of your website need more attention to improve crawl efficiency and content value.
Submission and Exclusion
The “Submitted and indexed” status is what you aim for; it means your page is in Google’s index and can appear in search results. Conversely, “Excluded” signals that specific URLs are intentionally left out of the index due to directives like ‘noindex’ tags or because they’re duplicates.
Knowing how these two differ guides you on ensuring valuable content gets indexed while managing less significant pages properly.
Soft 404 Errors
Lastly, Soft 404 errors significantly impact indexing as they mislead both users and crawlers into thinking a valid page exists when it doesn’t. These should be corrected promptly to avoid losing potential traffic from genuine pages being mistaken as nonexistent by search engines.
Identifying and Fixing Server Errors for URL Indexing
Common Errors
Server errors can block Googlebot from indexing your pages. The most common are 5xx server errors.
These errors mean your site’s server is failing to respond properly. This makes it hard for Google to index your pages. You might see these errors in the Google Search Console under “Coverage” issues.
Server Logs
Use server logs to find why indexing fails. These logs show how Googlebot interacts with your site.
Look for patterns of failed requests that match 5xx errors. This will help you understand what’s going wrong. Server logs are essential tools in diagnosing indexing issues.
Configuration Adjustments
Making changes to your server settings can solve many problems. Ensure that Googlebot isn’t accidentally blocked by firewall or security settings.
Adjustments might include increasing server capacity or fixing faulty scripts. Sometimes, simple changes like updating outdated software can make a big difference.
Addressing Robots.txt and ‘Noindex’ Tags
Verify Robots.txt
After tackling server errors, it’s crucial to check the robots.txt file. This file tells Googlebot which pages to crawl or ignore. Sometimes, important URLs might be mistakenly blocked.
To fix this, open your robots.txt file. Look for “Disallow:” entries. These lines block access to certain parts of your site. Make sure none of your valuable pages are listed here.
If they are, remove those lines or adjust them accordingly. This change will allow Googlebot to crawl these pages again.
Remove ‘Noindex’ Tags
Pages marked with ‘noindex’ tags tell search engines not to include them in search results. If you want a page indexed, ensure it doesn’t have this tag.
First, inspect the page’s HTML code. Look for <meta name="robots" content="noindex">. If you find this tag on a page you wish to index, delete it.
Next, check other meta robots tags on the page. Ensure they’re set up correctly for indexing purposes.
Meta Robots Configuration
Correctly configuring meta robots tags is essential for proper indexing.
These tags should reflect your intentions clearly:
-
For indexing:
<meta name="robots" content="index,follow"> -
To prevent indexing:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex,nofollow">
Review all key pages on your site. Make sure their meta robots tags align with your goals for those pages. Adjust any discrepancies promptly.
By carefully managing robots.txt files and ‘noindex’ tags while ensuring correct configuration of meta robots tags, you can significantly improve how well Google indexes your site. This proactive approach helps avoid common pitfalls that could hinder visibility in search results.
Resolving Redirect and Access Issues
Fix Redirects
Redirects can be tricky. They’re meant to take users from one page to another. But, if not set up correctly, they cause problems. Improper redirects might lead you in circles or to the wrong place.
To tackle this issue, first identify any redirect chains. These are series of redirects that send users hopping from one URL to another before reaching their destination. It’s a common mistake that can confuse Google’s crawlers too.
Next, look for infinite loop redirects. This is when a page redirects to another page that brings it right back. It’s like being stuck in a maze with no exit.
Check Parameters
URL parameters need attention as well. Sometimes they create duplicate content or access issues without us knowing it.
Start by reviewing how your site uses parameters.
-
Are they necessary?
-
Do they change the content on the page?
If parameters are causing duplicates, consider using the canonical tag or adjusting your website’s settings.
Remember, fixing these issues improves your site’s health and helps Google understand your pages better.
Enhancing Site Quality for Better Indexing
Website Speed
Improving your website loading speed is crucial. Fast-loading pages are more likely to be indexed by Google. Users and search engines prefer sites that load quickly.
To enhance speed, consider compressing images and using a content delivery network (CDN). These steps can significantly reduce loading times.
Mobile Friendliness
Ensure your site is mobile-friendly. With more people using mobile devices, Google prioritizes these sites for indexing. Check your site’s mobile compatibility in the Google Search Console.
Making your website responsive to various screen sizes improves user experience. This leads to better engagement and potentially higher rankings.
Content Quality
Eliminate thin content from your site. Focus on creating quality content that provides value to users. High-quality pages are more likely to get indexed and rank well in search results.
Consider the following tips:
-
Write detailed articles that cover topics thoroughly.
-
Use multimedia elements like images and videos to complement text.
-
Ensure all content is original and offers unique insights or information.
Optimizing Content and Internal Linking Structure
Relevant Keywords
Incorporating relevant keywords within your content is crucial. It helps Google understand what your page is about. This makes it easier for the search engine to index your pages properly.
When you add keywords, make sure they fit naturally into the text. Don’t force them in where they don’t belong. Your main goal should be to help people find what they’re looking for, not just to trick a search algorithm.
Internal Links
Internal links are another key factor in optimizing your site’s structure. They guide visitors through your website, leading them from one piece of content to another.
By linking related pages together, you distribute page authority more evenly across your site. This can boost the ranking potential of each individual page. Make sure every important page is accessible through internal links. A well-structured internal linking system can significantly improve crawlability.
Fresh Content
Updating stale content keeps it relevant and interesting both for users and search engines.
Consider revisiting old posts or pages every few months. Add new information or insights that have emerged since its initial publication. Not only does this practice keep your content fresh, but it also signals to Google that you’re actively maintaining the quality of your site.
Using the URL Inspection Tool for Indexing Errors
Diagnose Issues
The URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console is your first step. It helps find what’s wrong with your pages. You just need to enter the URL you’re having trouble with.
After entering the URL, you’ll see a detailed url inspection report. This includes whether Google has indexed the page, any errors, and when it was last crawled. If there are issues, like a wrong canonical URL or response code errors, they’ll show up here.
Re-index URLs
Once you’ve fixed these problems based on the tool’s feedback, submit these URLs for re-indexing directly through the tool. Click on “Request indexing” after ensuring all issues are resolved.
It’s simple but effective. Fix errors then ask Google to take another look at your page by submitting it again. Remember: only do this after making necessary changes.
Monitor Reports
After submission, keep an eye on coverage reports in the Search Console. These reports will tell if Google has successfully indexed your pages or not.
Look out for changes in indexing status under “Coverage”. Also, check for new warnings or errors that might pop up post-submission.
-
Use live url inspection often
-
Watch out for search console warnings and updates in coverage reports
Strategies for Improving Domain Rating and Backlink Profile
Guest Blogging
Engaging in guest blogging on reputable sites is a smart move. It boosts your site’s visibility. You share your expertise with a new audience. This can lead to more quality backlinks.
Find sites related to your niche. Reach out with a well-crafted pitch. Offer valuable content that their readers will love.
Broken Link Building
Use broken link building tactics next. This involves finding dead links on websites and suggesting your content as a replacement. It helps website owners fix broken links while you get a backlink.
Start by using tools to find broken links in your niche. Contact the website owner with your content as an alternative.
Audit Backlinks
Regularly auditing your backlink profile is crucial. Identify harmful links that could affect your domain rating.
-
Use tools to analyze incoming links.
-
Look for spammy or irrelevant sites linking to you.
-
Disavow harmful links through Google Search Console.
Summary
You’ve got the lowdown on making sure your pages shine in Google’s eyes, from squashing those pesky server errors to ensuring your content is top-notch. It’s all about giving your site the TLC it deserves, whether that’s by playing nice with robots.txt or beefing up your domain’s street cred with a killer backlink profile. Remember, fixing pages not indexed by Google isn’t just a one-and-done deal; it’s an ongoing mission to keep your site in tip-top shape.
So, what’s next? Roll up those sleeves and dive into action. Use the insights and strategies we’ve shared as your toolkit to tackle those indexing issues head-on. Your website’s visibility is in your hands, and with a bit of elbow grease and dedication, you’ll see those pages lighting up the search results in no time. Let’s make your site impossible for Google to ignore!
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if my page is not indexed by Google?
Check your URL’s indexing status directly in the Google Search Console. If it says “Page not indexed,” you’ve got some digging to do!
Why would a server error affect my page’s indexing?
Server errors can stop Google’s bots in their tracks, making them unable to crawl and index your page. Think of it like a roadblock on the internet highway.
Can robots.txt or ‘Noindex’ tags be why my site isn’t indexed?
Absolutely! If your robots.txt file tells search engines to keep out, or if a ‘Noindex’ tag is present, they’ll obey those commands like good little bots.
What should I do if redirects are messing with indexing?
Ensure that any redirects are set up correctly. Incorrectly configured redirects can lead to confused crawlers wandering away from your content.
How does enhancing site quality help with indexing?
A high-quality site is like a catnip for Google’s algorithms. The better the content and user experience, the more likely it will get indexed.
Why is optimizing content important for indexing?
Optimized content speaks Google’s language fluently, helping its bots understand and index your pages more effectively. It’s all about communication!
How can improving my domain rating aid in getting pages indexed?
A stronger domain rating signals trustworthiness and authority to search engines, making them more inclined to index your pages. It’s like having a VIP pass at a nightclub – doors open easier.